Google announced in November 2016 that it was working on a new mobile-based indexing system: Google Mobile First. What does that mean? How does Google indexing a site currently work, and what will Mobile-First change?
Indexing is the basis of natural referencing on Google. Understanding how it works allows you to technically optimize a website for SEO. Find out more about this process, as well as tips on how to improve your site's indexing and prepare for Google Mobile First.
If you want the best SEO Services in Pakistan, contact us.
The Steps of Indexing a Web Page
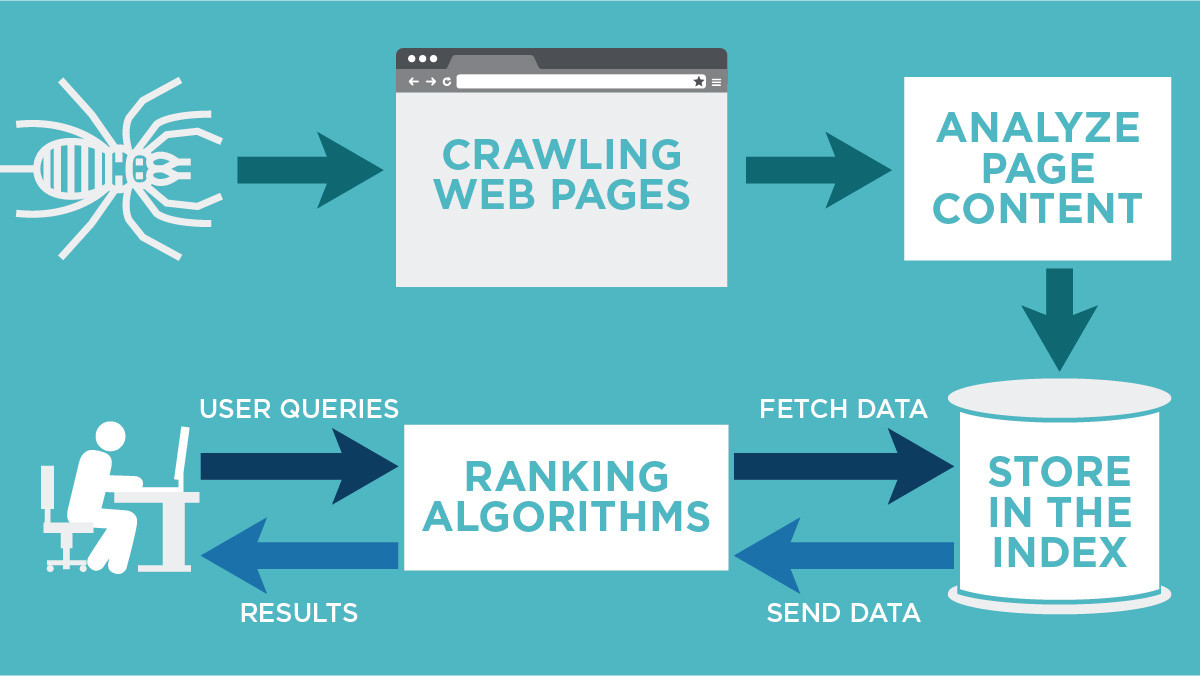
Indexing is Google's process of recording pages and their content in its database to classify them and then display them in its results according to Internet users' requests.
For this, Google sends computer programs called crawlers (also called spider or Google bots) to crawl web pages. These robots copy the content of the pages into Google's database (the index). This content is analyzed to compare it with other content in the database and define a ranking (positioning) of the most relevant content about Internet users' requests.
What Can Stop The Indexing of The Pages of a Website?
To find pages to crawl and index, Google's indexing robots use several means:
- links between pages (internal or external)
- the sitemap.xml file
- URLs sent via the Google Search Console tool
- Google Chrome (?)
Also, Google's robots have a "crawl budget" (the crawl being the act of visiting pages). This budget is important to consider for websites with several thousand pages to promote indexing.
Because Google bots do not necessarily index all the pages, they visit! In some cases, they may not index a URL for different reasons:
- The URL was not visited for one or more reasons: insufficient crawl budget, no link to the page, URL not present in the sitemap, etc.
- The URL is in soft 404 error
- The URL has duplicate content, internal or external
- The URL presents a meta robots noindex code
- The robots.txt file blocks Googlebot's access to certain URLs
- The content of the page is not sufficient to merit indexing according to Google's criteria
Thus, to ensure that there is every chance that all the important pages of the website are indexed, several technical and structural rules must be respected:
- Fix 404 errors to avoid wasting crawl budget
- Create an internal link to encourage visits to important pages
- Check that the robot meta tag of the pages and the robots.txt file are not blocking indexing
- Make sure the tree is not too deep (more than 4 or 5 clicks to reach a page)
- Avoid internal duplicate content
The more pages your website has, the more it crawls, and its indexing pages by Googlebot may be complex or long. For the pages important for the SEO strategy, it may be interesting to offer them for indexing when they are put online using the Google Search Console tool (Exploration menu> Explore like Google).
Google Mobile First, What Will it Change in SEO?
Currently, it is the web version of the site that is indexed and used for positioning. Googlebot visits and indexes web URLs, and these are then positioned on Google's desktop and mobile search results according to SEO criteria.
With Google Mobile First, the principle is the same, but it is the MOBILE version of the site that will be indexed and used for positioning.
So this poses several questions for SEO:
- What will happen if a site does not have a web version? It will still be indexed, but will it be positioned behind sites with a mobile version?
- The mobile version often has less text to lighten the pages. Will SEO be done with less text?
- Are some SEO criteria going to change?
- Mobile versions currently often have little content. What will be the most visible between a non-mobile compatible website and a non-SEO optimized mobile site?
If the mobile version's content becomes that used to position a site, one thing is for sure; you need a mobile-friendly site! And if you already have one, to keep the current positioning of the website, it is best to make sure that the textual content and SEO tags are the same on both versions.
What Type of Mobile Version?
In terms of the method used for mobile compatibility, Google has no preference, as long as the site can be correctly visited from a mobile. You can, therefore, use responsive design or a dedicated mobile version.
Responsive design has the advantage of avoiding having to manually transfer the website's content to the mobile version. Still, it sometimes requires more work at the technical level in the case of advanced layouts. The responsive being rather made to adapt a site to all screen sizes, its ergonomics are not designed for mobile natively, which can sometimes pose ergonomic problems.
Of course, we will have to consider the browsing habits of mobile users for natural referencing. Adding a lot of text on a mobile version can affect navigation ease, so you will have to think about how to integrate this content without harming the mobile ergonomics. So integrate graphic designers, web designers, and ergonomists into this project.
Do you want to support upgrading or creating the mobile version of your site for Google Mobile First? Our graphic designers and SEO experts will make recommendations to you to create a mobile-friendly site that is well referenced and pleasant to use!